Unveiling the Dynamic Duo: Olmesartan/Amlodipine
As a fellow human navigating through life with my furry friends, Ollie and Nimbus, I've often marveled at the fascinating parallels between our health issues. I mean, yes, I'm comparing human and pet health here, but stick with me. Just like humans, animals, like my adorable Goldendoodle, can suffer from hypertension related to diabetes. This surprising similarity got me thinking about the various medications available to manage this condition. The one that stood out, both for its effectiveness and its unique combination, is Olmesartan/Amlodipine. Today, I've decided to dive in and shed some light on this dynamic duo.
A Peek into the World of Diabetes-Related Hypertension
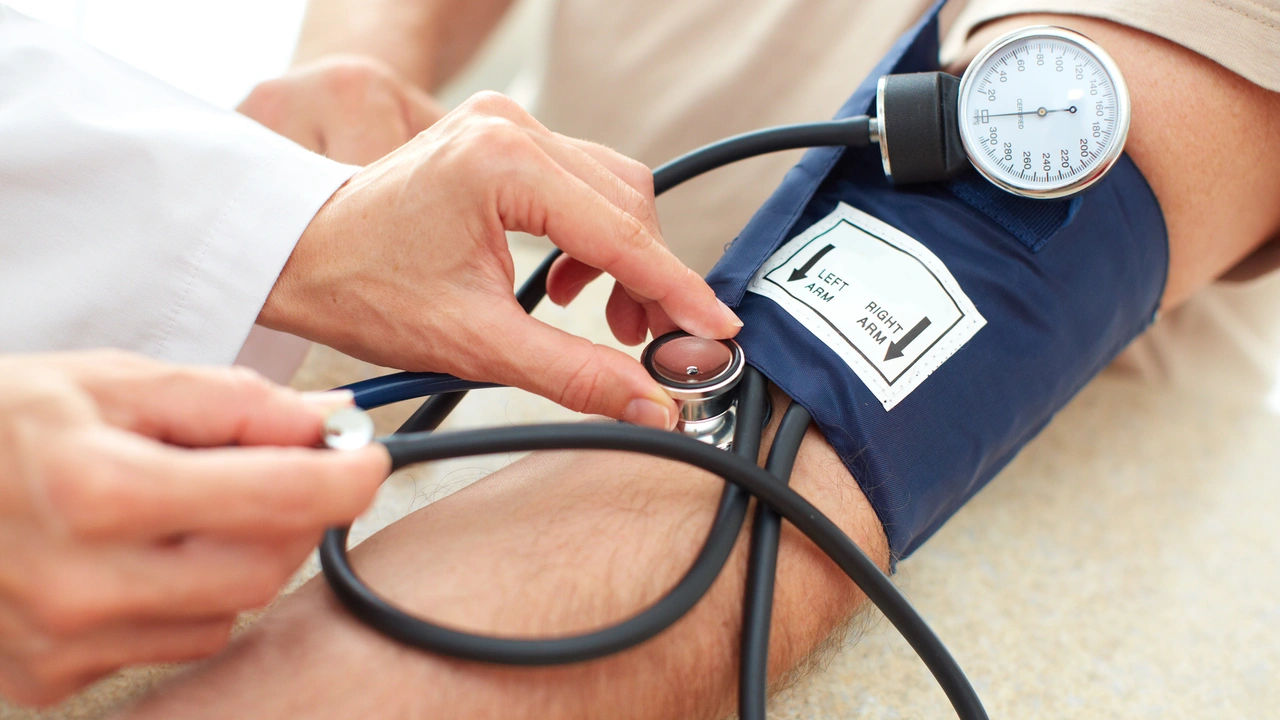
Before we delve into the role of Olmesartan/Amlodipine, let's take a quick tour of the broader picture. Hypertension, in simple terms, is high blood pressure, a health condition that affects a large number of people worldwide. In the diabetic community, it isn't just a notorious lurker; it's an uninvited guest that cranks up the risk of complications. Diabetes and hypertension together? Sounds like a nasty tag team, doesn't it? Well, they are. They often work in unison to speed up the progression of cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and stroke. This is why maintaining blood pressure within a healthy range is vital for individuals with diabetes.
Why Olmesartan/Amlodipine Stand out in the Crowd
Now that we've familiarized ourselves with the opponent, let’s introduce our tag team: Olmesartan and Amlodipine. Both of these medications are stand-outs on their own but when paired together, they form a powerful bulldozer that helps to manage blood pressure effectively. The question is, why this specific combination? Well, the beauty of this combo lies in their complementary nature; how each medication tackles a different piece of the hypertension puzzle. Just like when Ollie teams up with Nimbus to elicit extra cuddles from me, Olmesartan and Amlodipine similarly combine their strengths to yield stronger effects.
Taking a Closer Look at Olmesartan
First up, we have Olmesartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, a real mouthful to pronounce! Its role is primarily to block the effect of a hormone called angiotensin II, which tends to narrow blood vessels. When this hormone's action is obstructed, blood vessels can relax and widen, which helps to reduce blood pressure. In simpler terms, it's like Ollie using his wily charm to persuade Nimbus to stop causing mischief and relax instead. It's a mediator helping to keep things calm and running smoothly.
Amlodipine: The Other Half of the Power Duo
Amlodipine, our second hero of consideration, is a calcium channel blocker. While it might sound like it's preparing for a medieval siege, its job is essentially to prevent calcium from entering certain tissues and arteries. The result of this blocking action? A more relaxed and open blood vessel system, which in turn lowers blood pressure. Essentially, Amlodipine is like Ollie sneaking in and gently swiping away Nimbus's favourite toy, allowing for a more peaceful atmosphere (until Nimbus notices, of course).
The Winning Combination: Olmesartan/Amlodipine in Action
Now imagine what happens when Olmesartan and Amlodipine join forces. They simultaneously work on different aspects of the hypertension issue, creating an overall more powerful response. This team work is somewhat similar to the noticeable increase in adorableness when Ollie and Nimbus decide to snuggle together, instantly melting my heart. Similarly, this combined effect of Olmesartan and Amlodipine can effectively manage hypertension in individuals with diabetes, mitigating risks and potentially preventing dreaded complications. They are, in essence, a dynamic duo, each enhancing the power of the other to create an overall stronger medication for combating diabetes-related hypertension.

KALPESH GANVIR
November 10, 2023 AT 17:12Jessie Bellen
November 12, 2023 AT 04:12April Barrow
November 13, 2023 AT 02:48lisa zebastian
November 13, 2023 AT 18:11Jasmine L
November 15, 2023 AT 00:54maria norman
November 16, 2023 AT 14:22Richie Lasit
November 18, 2023 AT 05:58Melody Jiang
November 19, 2023 AT 03:59Iris Schaper
November 19, 2023 AT 06:07Dipali patel
November 19, 2023 AT 12:24Justice Ward
November 20, 2023 AT 07:06bhuvanesh kankani
November 20, 2023 AT 15:53Jo Sta
November 21, 2023 AT 14:47Harrison Dearing
November 22, 2023 AT 04:07Jasmine Kara
November 23, 2023 AT 20:01arthur ball
November 25, 2023 AT 15:49